Can Acceleration Be Non Zero When Velocity Is Zero
Here between the time intervals of 0-2 seconds the velocity of the particle is increasing with respect to time. A van accelerates uniformly from a velocity of 10 m s-1 to 20 m s-1 in 25 s.
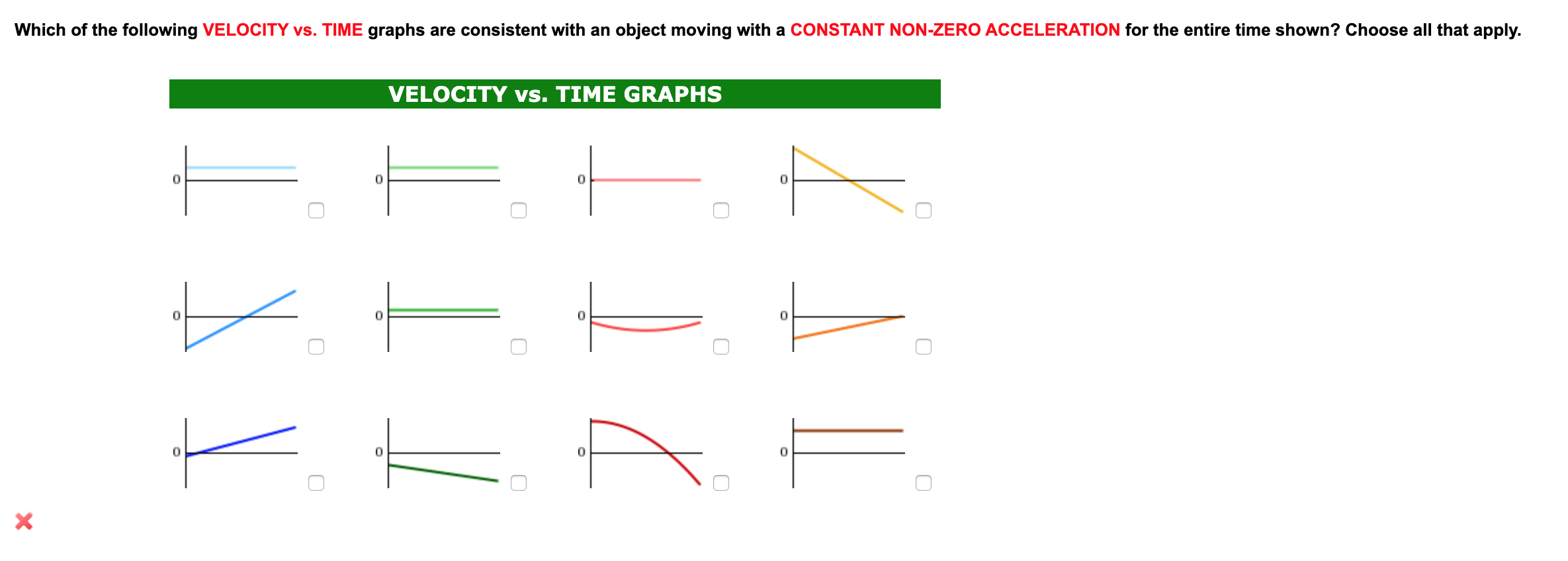
Solved Which Of The Following Velocity Vs Time Graphs Are Chegg Com
Jerk is felt as the change in force.

. Velocity does not suddenly switch on but instead grows from zero. Any object in motion has acceleration. The velocity of any point on a body undergoing general plane motion can be determined easily often with a scalar approach once the instantaneous center of zero velocity of the body is located.
The basic equation for solving this is. The approach NM is used to compute the structural frequency responses in a frequency interval. Since taking the derivative of the velocity function produces.
For example when a vehicle starts from a standstill zero velocity in an inertial frame of reference and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds it is accelerating in the direction of travel. Also in this example when acceleration is positive and in the same direction as velocity velocity increases. If the objects velocity is changing the object is either accelerating or decelerating.
If any of the components of the acceleration are zero then that component of the velocity would be a constant. What is the acceleration of the van. If you know any 3 of those things you can plug them in to solve for the 4th.
Non uniform acceleration. Acting on it is zero. Since the body seems to rotate about the IC at any instant as shown in this kinematic diagram the magnitude of velocity of any arbitrary point is.
Hence the body is experiencing a positive acceleration as the slope of the v-t curve in this time interval is positive. A speedy vehicle with an acceleration undergoes non-uniform motion. D vt 12at 2 where d is distance traveled in a certain amount of time t v is starting velocity a is acceleration must be constant and t is time.
Displacement velocity and acceleration responses of the structures in a frequency interval are considered as the objective function. The motion of a truck on the highway with constant speed. Between the time intervals of 2-3 seconds the velocity of the object is.
Consider the velocity-time graph shown above. Initial velocity u 10 ms-1 Final velocity v 20 ms-1 Time taken t 25 s. Acceleration without jerk is just a consequence of static load.
From the above table we understand that in uniform. From Calculus I we know that given the position function of an object that the velocity of the object is the first derivative of the position function and the acceleration of the object is the second derivative of the position function. A car travelling at 24 m s-1 slowed down.
At terminal velocity the object moves at a steady speed in a constant direction because the resultant force. In applicable terms. For example a skydiver falling spread-eagled through the air.
The proposed computing method can adaptively and accurately calculate the structural frequency responses as the design variables are updated. If the vehicle turns an acceleration occurs toward the new direction. Positive negative and zero acceleration.
The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared ms 2. If a b and c are not zero then the velocity function must be linear in time. Acceleration Using A Velocity Time Graph Example Problems With Solutions.
Similarly acceleration does not suddenly. Find a the velocity and acceleration of the particle as functions of time b the velocity and acceleration at t 20 s c the time at which the position is a maximum d the time at which the velocity is zero and e the maximum position. The zero of the acceleration function corresponds to the maximum of the velocity in this example.
So there must be some acceleration involved. Jerk can be felt as an increasing or decreasing force on the body. The acceleration vector is constant and doesnt change with time.
How is Uniform Motion Different from Nonuniform Motion. If the object has constant velocity the objects acceleration is zero. Section 1-11.
This gives you the distance traveled during a certain amount of time. In this section we need to take a look at the velocity and acceleration of a moving object. If an object is moving at a constant speed following a circular path the object experiences a constant acceleration that.
As acceleration tends toward zero eventually becoming negative the velocity reaches a maximum after which it starts decreasing.

Homework And Exercises Why Isn T Acceleration Always Zero Whenever Velocity Is Zero Such As The Moment A Ball Bounces Off A Wall Physics Stack Exchange

Kinematics Can We Have Zero Acceleration And Non Zero Velocity Quora

Kinematics The Instant An Accelerating Object Has Zero Speed Is It Speeding Up Slowing Down Or Neither Physics Stack Exchange
Kinematics Can We Have Zero Acceleration And Non Zero Velocity Quora
Comments
Post a Comment